Rendering and Ranking | Search engine basics
Let's learn the multiple methods of Rendering our websites in client browsers and How multiple factors affect the Rankings of our websites.

JavaScript is an important part of the web development ecosystem. In the past, most programming languages were sending all content directly from the server.
With technology like JavaScript, fetching information from the browser became more popular than ever. This, in turn, affected search engines and their ability to understand pages, as most bots were only parsing the initial HTML from the server and loading it to the browser.
Some main factors on the Rendering and Ranking of our websites.
- Rendering Strategies
- AMP
- URL Structure
- Metadata
- On Page SEO
Let's see them in detail. I may take the example of Next.js in multiple sections because I like the Next.js framework which fits all the requirements for our SEO.
Rendering strategies
Just a term to define multiple ways of Rendering websites.
Static Site Generation (SSG)
Static site generation is where your HTML is generated at build time. This HTML is then used for each request. Static site generation is probably the best type of rendering strategy for SEO as not only do you have all the HTML on page load because it's pre-rendered, but it also helps with page performance – now another ranking factor when it comes to SEO.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
Like SSG, Server-Side Rendering (SSR) is pre-rendered, which also makes it great for SEO. Instead of being generated at build time, as in SSG, SSR's HTML is generated at request time. This is great for when you have very dynamic pages.
Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR)
If you have a very large amount of pages, generating them all at build time may not be feasible. Next.js allows you to create or update static pages after you have built your site.
Incremental Static Regeneration enables developers and content editors to use static generation on a per-page basis, without needing to rebuild the entire site. With ISR, you can retain the benefits of static while scaling to millions of pages.
Client-Side Rendering (CSR)
Client-Side Rendering allows developers to make their websites entirely rendered in the browser with JavaScript. On the initial page load, a single HTML file is generally served with little to no content until you fetch the JavaScript and the browser compiles everything.
As we commented above, in general, Client-Side Rendering is not recommended for optimal SEO.
CSR is perfect for data-heavy dashboards, account pages, or any page that you do not require to be in any search engine index.
Rendering strategies summary
The most important thing for SEO is that page data and metadata are available on page load without JavaScript. In this case, SSG or SSR are going to be your best options.
One of the major strengths of Next.js is that each one of the above rendering methods can be done on a per-page basis. You might want your blog posts statically generated, your customer's account dashboard client-side rendered, and then perhaps you have a news feed you want to server-side render.
AMP
In 2016, Google began giving search ranking preference to web pages using AMP – a technology that enables developers to create web pages that load faster on mobile devices – at the cost of building and maintaining them over time.
With the Core Web Vitals page experience update, Google dropped AMP pages as a requirement to appear in search carousels. This is one of the last main benefits that Google had for AMP in terms of SEO purposes.
Since the introduction of AMP, newer technology, such as Next.js, has proven its ability to improve website experience without sacrificing Developer Experience (DX).
URL Structure
URL Structure is an important part of any SEO strategy. While Google doesn't disclose which weight each part of SEO has, great URLs are considered a best practice no matter if they are a big or small ranking factor in the end.
You might want to follow some principles:
- Semantic: It's best to use URLs that are semantic, meaning that they use words instead of IDs or random numbers. Example:
/learn/basics/create-nextjs-appis better than/learn/course-1/lesson-1. - Patterns that are logical and consistent: URLs should follow some sort of pattern that is consistent among pages. For example, you want to have a folder that groups all product pages, instead of having different paths for each product that you have.
- Keyword focused: Google still bases a considerable part of its systems on the keywords a website contains. You might want to use keywords in your URLs to facilitate understanding the purpose of the pages.
- Not parameter-based: Using parameters to build your URLs is generally not a good idea. They are not semantic in most cases, and search engines might confuse them and demote their rankings in results.
Metadata
Metadata is the abstract of the website's content and is used to attach a title, a description, and an image to the site.
Title
The title tag is one of the most important SEO elements for two main reasons:
- Firstly, it's what users see when they click to enter your website from search results.
- Secondly, it's one of the main elements Google uses to understand what your page is about. Using keywords in the title is recommended because it usually leads to increased improved ranking positions in search engines.
Here's an example:
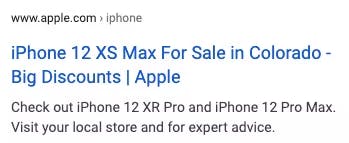
<title>iPhone 12 XS Max For Sale in Colorado - Big Discounts | Apple</title>
This page contains all the main keywords and also makes it attractive for users showing a clear value proposition: Discounts!
Description
The description meta tag is another important SEO element, but less so than the title. According to Google, this element is not taken into account for ranking purposes, but it can affect your click-through-rate on search results.
Use the description meta tag to complement the information in your title. Work in more keywords to the content here if some didn't fit in the title. These keywords will appear in bold if a user's search contains them.
An example of a description meta tag in HTML:
<meta
name="description"
content="Check out iPhone 12 XR Pro and iPhone 12 Pro Max. Visit your local store and for expert advice."
/>
This is how it looks on the page when it's part of the search engine results page (SERP):
Open Graph
The Open Graph protocol, originally developed by Facebook, standardizes how metadata is used on any given web page. You can provide as little or as much information as you would like, but all of the open graph pieces fit together to create a representation of the site it's attached to.
Other social media companies (like Pinterest, Twitter, LinkedIn, etc), may also use the open graph for displaying rich cards when sharing a URL. Twitter also has tags for its Twitter Cards.
While these Open Graph tags have a lot of similarities with SEO-related tags, they do not offer any benefit to search engine rankings, but they are still recommended to use as people might share your content on social media or private messaging tools such as WhatsApp or Telegram.
<head>
<title>Cool Title</title>
<meta name="description" content="Checkout our cool page" key="desc" />
<meta property="og:title" content="Social Title for Cool Page" />
<meta
property="og:description"
content="And a social description for our cool page"
/>
<meta
property="og:image"
content="https://example.com/images/cool-page.jpg"
/>
</head>
Having a shareable link that offers a description and title, along with a picture that represents the page's content does not have a direct effect on SEO rankings, but it indirectly increases the clickability of the link, which will ultimately lead to more visitors to your site.
On Page SEO
At a high level, on-page SEO refers to the headings and links that make up the overall structure of the page. Headings indicate importance in the document and links connect the web together.
Headings and H1
Headings help users understand the structure of a page and what they are going to read in the next paragraphs. They also facilitate the search engine's job of understanding which parts of the page are the most important.
Headings go from 1-6 and Heading 1 tends to be thought of as the most important. It's recommended to use the H1 heading tag on each page. H1 should represent what the page is about and be similar to your title tag.
function Page() {
return <h1>Your Main Page Heading</h1>
}
Internal Links
The internet is connected by links. Without links from one website to another, the internet probably wouldn't exist. Websites that receive more links tend to represent websites that are more trusted by users. Google started this principle with the invention of the PageRank Algorithm.
The PageRank algorithm, at a high level, is an algorithm that goes through every link on a database and scores domains based on how many links they receive (quantity) and from which domains (quality). Lots of links from spam websites most likely have little to no value.
A link from a big national press website, however, is likely very valuable for search engines. This is why links are important and you should always include them both internally between your page, and also externally to other websites. Links always need to use href in order to be used for PageRank calculations.
Conclusion
These were the main factors affecting the Rendering and Ranking of our websites.Let me know if I missed something.
Thank you for reading my blog/article. ❤️❤️
